2026 is here! And guess what- it’s pretty hard to imagine any business without dedicated software, right?
Well, that’s the point exactly! But here’s the catch!
Though many businesses are trying to get into software development, not everyone can succeed.
But why?
The answer lies in the fact that they forget one important aspect, i.e., “Agile software design process”!
Did you know?
The global software development market is expected to go beyond $898 billion by 2029. (Source: Statista).
Sounds interesting, doesn’t it?
But now the question arises – What is the best way to approach software design? What is the design phase of the software development life cycle?
Without further ado, let’s dive in!
What is Software Designing?
To put it simply, Software design is the process of planning and structuring a software system before actual coding begins. It involves defining the architecture, components, interfaces, and data flow to ensure the software meets user requirements while being efficient, scalable, and maintainable. Designers use principles like modularity, abstraction, and reusability to break down complex systems into manageable parts. By doing so, they create a blueprint that guides developers in writing clean, structured, and error-resistant code.
In practice, software design goes beyond technical diagrams; it bridges user needs with engineering solutions. Professionals apply design methodologies such as object-oriented design, structured design, or agile modeling to align the system’s functionality with business goals. They also factor in performance, security, and usability to ensure the end product is reliable and user-friendly.
A strong design phase reduces development risks, minimizes costly rework, and lays the foundation for long-term software success.
Key Elements of an Effective Software Design System
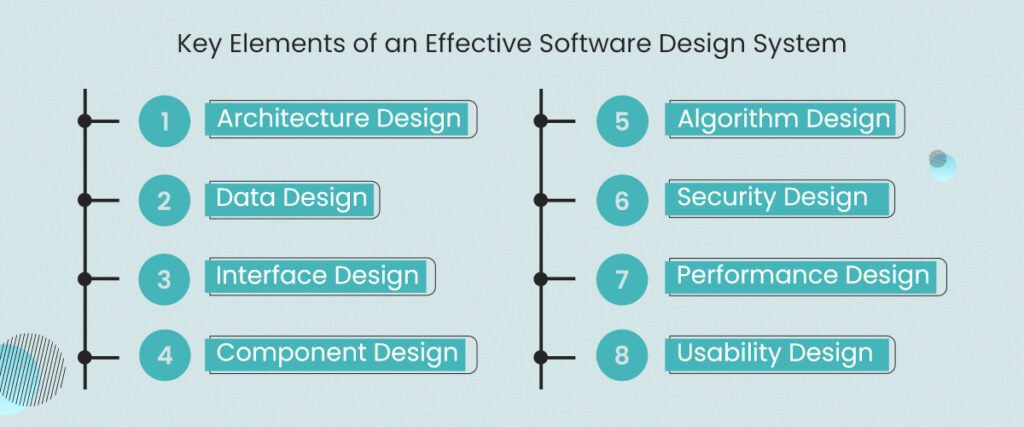
1. Architecture Design
Defines the overall structure of the software, including how different modules, components, and layers interact. It sets the foundation for scalability, maintainability, and performance.
2. Data Design
Focuses on how data is stored, processed, and managed within the system. This software design process element includes database schemas, data flow diagrams, and data integrity rules to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
3. Interface Design
Covers both user interfaces (UI) and system interfaces. It specifies how users will interact with the system and how different software components or external systems communicate.
4. Component Design
Breaks the system into individual components or modules, each with specific functionality. This ensures modularity, reusability, and easier debugging or upgrading.
5. Algorithm Design
Defines the step-by-step logical procedures the system uses to process data and execute tasks. Efficient algorithm design improves system speed and resource usage.
6. Security Design
Incorporates measures like authentication, authorization, and data encryption to protect the system from vulnerabilities and ensure data privacy.
7. Performance Design
Considers factors like response time, resource optimization, and scalability to ensure the software can handle varying loads without degradation.
8. Usability Design
Ensures the system is user-friendly, intuitive, and aligned with user expectations. It includes layout, accessibility, and user experience (UX) considerations.
Software Design and Development Process: Step-by-Step Explanation
The software design and development process is a structured approach that guides how software is planned, built, tested, and maintained. This process typically involves the following stages:
#1. Requirement Analysis
In the software design and development process, the first step is analyzing user needs and business requirements. Teams gather insights from stakeholders, document expectations, and identify core functions the software must fulfill. A clear requirement analysis avoids confusion later, sets measurable goals, and forms the foundation for a successful design process in software engineering.
#2. Planning the Design Phase
The design phase of the software development life cycle transforms requirements into actionable plans. Designers map out system architecture, data models, and workflows. They decide on technologies, interfaces, and security protocols to be used. This step emphasizes clarity and detail, helping ensure the software meets performance expectations while remaining scalable and maintainable in the long run.
#3. Creating Architectural and Component Designs
During the software design process, professionals divide the system into smaller components and define their relationships. This involves both architectural design (overall structure) and component design (specific modules). A modular approach enables reusability, easy debugging, and faster updates. It is considered the best way to approach software design for complex and evolving systems.
#4. Adopting Agile Practices
Many organizations now prefer the agile software design process because it allows iterative improvements. Instead of finalizing everything up front, teams design, build, and test in short cycles. This method ensures flexibility, quick responses to client feedback, and faster delivery of functional software. It aligns perfectly with modern businesses that face rapidly changing requirements.
#5. Implementation and Coding
After completing the design process in software engineering, the design blueprint transitions into actual coding. Developers use programming languages and frameworks best suited to the project. By following design specifications strictly, they ensure the system’s functionality matches what was initially planned, reducing the risk of costly rework during later stages of development.
#6. Testing and Quality Assurance
A crucial step in the software design and development process is testing. Teams conduct unit tests, integration tests, and system tests to validate functionality and performance. This phase ensures that the application is free from critical errors, secure against vulnerabilities, and optimized for usability, delivering a reliable product to end-users.
#7. Deployment and Maintenance
Once testing is complete, the software is deployed into the production environment. However, the design phase of the software development life cycle doesn’t end here. Continuous monitoring, updates, and bug fixes are essential for long-term success. Maintenance ensures that the software adapts to new technologies and changing customer demands.
#8. Using the Best Software for Software Design
For efficiency, teams rely on tools and platforms considered the best software for software design. Examples include UML modeling tools, wireframing software, and architecture design platforms. These tools help create detailed visual models, streamline collaboration, and reduce errors. Choosing the right design tools accelerates development and improves communication among stakeholders.

Popular Software Design Models and Approaches
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to software design. Different projects demand different models depending on complexity, timeline, and business goals. Here’s a clear comparison of the most widely used software design models and approaches.
1. Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model follows a linear sequence: requirements, design, development, testing, and deployment. It works best for projects with fixed requirements and minimal changes, such as internal tools or compliance-driven systems. However, its rigidity makes it less suitable for dynamic or evolving applications.
2. Agile Model
The agile software design process focuses on iterative development and continuous feedback. Teams design, build, and test in short cycles, allowing quick adjustments. Agile works best for startups and fast-changing business environments where flexibility and speed are critical.
3. Spiral Model
The Spiral model combines iterative development with risk analysis. Each cycle focuses on identifying and mitigating potential risks before moving forward. It’s ideal for large, complex systems where performance, security, and reliability are high priorities.
4. Object-Oriented Design (OOD)
Object-oriented design organizes software around objects and classes. This approach promotes modularity, reusability, and scalability. It’s widely used in modern software systems and aligns well with agile development practices.
5. DevOps-Oriented Design
DevOps integrates design with continuous deployment and monitoring. It focuses on automation, collaboration, and rapid releases. This approach is best suited to cloud-based applications and systems that require frequent updates and high availability.
What are the Best Software Design Tools?
The right tools can significantly improve efficiency, collaboration, and accuracy during the software design process. Today’s teams rely on a mix of visual, architectural, and collaboration tools to streamline work.
- UML & Modeling Tools
Tools like Lucidchart, Draw.io, and Visual Paradigm help teams create UML diagrams, flowcharts, and system architectures. These visuals make complex systems easier to understand and communicate.
- UI/UX Design Tools
Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch are widely used for interface design and prototyping. They allow designers and developers to collaborate in real time, test user flows, and refine designs before development starts.
- Architecture & System Design Tools
Tools like Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect and C4 Model frameworks help architects plan scalable and maintainable systems. They are especially useful for enterprise applications with complex dependencies.
- Collaboration & Documentation Tools
Confluence, Notion, and Miro help teams document design decisions, user stories, and workflows. Clear documentation ensures continuity and reduces confusion during development and maintenance.
- Code & Design Integration Tools
Modern IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA and Visual Studio integrate design principles directly into coding environments, ensuring consistency between design and implementation.
Choosing the best software for software design depends on project size, team structure, and complexity, but using the right tools always leads to better outcomes.
What are the Mistakes to Avoid During the Software Design Lifecycle?
1. Ignoring User Requirements
Failing to understand or properly document user needs often results in a product that doesn’t solve the actual problem. Always validate requirements with stakeholders before starting the design.
2. Overcomplicating the Design
Adding unnecessary features or complex structures makes the system harder to build, maintain, and scale. Stick to simplicity and focus on solving the core problem effectively.
3. Lack of Modularity
Designing without modular components leads to tightly coupled systems that are difficult to debug, test, or upgrade. Ensure the design follows modular and reusable principles.
4. Neglecting Scalability
Not planning for future growth can cause performance issues when user demand increases. Build with scalability in mind, even if the initial system is small.
5. Poor Data Design
Ignoring proper database structure, data flow, and integrity checks can lead to bottlenecks, redundancy, or data loss. Invest time in solid data modeling.
6. Overlooking Security
Failing to integrate security measures like authentication, encryption, and access control during design makes the software vulnerable to threats. Security must be built in, not an afterthought.
7. Skipping Documentation
Not documenting design decisions and structures makes it difficult for future developers to understand and maintain the system. Maintain clear diagrams, notes, and guidelines.
Real-World Software Design Process Example (Retail Use Case)
Let’s move away from theory for a moment and talk about what actually happens in the real world.
Imagine this: a growing retail business is juggling spreadsheets, emails, and disconnected tools to manage inventory and orders. Mistakes happen. Stock goes missing. Orders get delayed. Customers complain. Sound familiar?
So the company decides, it’s time to build a custom software system. But where do they start?
Step 1: Understanding the Real Problem
Before writing any code, the team asks the most critical question: What’s broken?
Warehouse managers want real-time stock updates. Sales teams need accurate order statuses. Finance wants clean reports. This is the requirement analysis phase, where every pain point is documented and clarified.
Skipping this step? That’s how projects fail before they even begin.
Step 2: Designing the Blueprint
Next comes the design phase of the software development life cycle. Architects create system diagrams showing how the frontend, backend, and database will communicate. Designers map out user flows, how an order moves from placement to delivery. UI wireframes show how each dashboard will look.
At this stage, the team asks: Is this simple enough for daily use? Can it scale if orders double next year?
Step 3: Breaking It into Modules
Instead of building one massive system, the software is divided into modules – inventory tracking, order processing, reporting, and user management. This modular approach makes the system easier to update and maintain. Want to add analytics later? No problem.
This is one of the most significant advantages of following a structured software design process.
Step 4: Applying Agile in Action
Rather than building everything at once, the team follows an agile software design process. They release a basic version of the inventory module first. Warehouse staff test it. Feedback comes in. Changes are made. Then the next module rolls out.
Why wait months to discover something doesn’t work when you can fix it in weeks?
Step 5: Testing, Refining, and Improving
Every iteration goes through testing. Does the system slow down under load? Are reports accurate? Is the interface intuitive? Each question leads to refinements that improve performance, usability, and reliability.
Final Thoughts
So, there you have it! That’s a wrap to the software design process in 2026! Designing software is more than just writing code; it’s about creating a solid foundation that balances functionality, usability, scalability, and security. A well-thought-out software design process minimizes risks, reduces costs, and ensures that the final product truly delivers value to its users.
If you’re looking for a trusted partner to bring your software ideas to life, EitBiz can help. With expertise in software design, development, and digital transformation, our software development experts deliver solutions that are tailored to your business goals and built for growth. Do you want the best design process in software engineering? If so, connect with EitBiz and make a captivating software design that engages and drives conversions.
FAQs
1. What are the main steps in the software design process?
The software design process usually starts with understanding what users actually need. Once requirements are clear, the team plans the design, creates system architecture and component layouts, and then moves into development. After that, the software goes through testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. Each step plays an important role, and skipping any of them often leads to confusion, delays, or costly fixes later.
2. Why is the design phase critical in the software development life cycle?
The design phase is where ideas turn into a clear plan. It helps teams visualize how the software will work before coding begins. When design is done properly, developers know exactly what to build, users get what they expect, and problems are caught early. Without a strong design phase, projects often face rework, budget overruns, and performance issues down the line.
3. What is the best software design approach for modern applications?
There isn’t one perfect approach that works for every project. However, most modern applications benefit from an agile software design approach. Agile allows teams to design and improve software in small steps, respond to feedback quickly, and adapt to changes without starting over. When combined with modular and user-focused design, it helps create flexible and scalable applications that grow with the business.
-

Sandy K is the dynamic and visionary Director at EitBiz. With a rich tapestry of experience spanning almost 15 years, Sandy has cultivated a unique, global perspective that he brings to the forefront of EitBiz’s operations.
View all posts
Visit Linkedin




